Solution-Biology questions, Select the viruses below that
Question 1: Select the viruses below that would be able to replicate if you injected only their genome into a permissive cell line (Hint: You should be able to answer this question by looking up the Baltimore classificaton of each virus)?
Answer
- A. Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- B. Rhinovirus
- C. Hepatitis C Virus
- D. Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- E. Influenza Virus
Question 2: Deep sequencing of a human clinical sample containing a potentially new virus contains sequence of the following genes. Indicate whether each gene can be of viral origin only, host cell only or both.
Answer
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
Read Answer Items for Question 2
ribosomal RNA
Read Answer Items for Question 2
ATP Synthase
Read Answer Items for Question 2
tRNA
Read Answer Items for Question 2
DNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
Read Answer Items for Question 2
Answer
A. Viral or Host
B. Viral Only
C. Host Only
Question 3: During synthesis of a single copy of its genome, reverse transcriptase creates a mutation in the HIV genome that would result in an inactive reverse transcriptase. This copy of the genome is still incorporated into a new viral particle and infects another cell. Will this new viral particle be able to replicate in its new host cell?
Answer
o It will not be able to replicate and produce new infectious viral particles
o It will be able to replicate and produce new infectious viral particles.
Question 4: Which of the following virus types may have segmented genomes
Answer
A. ss (+) RNA
B. ss (-) RNA
C. ds RNA
D.ss (+) DNA
E.ds DNA
Question 5: Match the pictures or descriptions of symmetrical virus structures with the type of structure depicted.
Answer
Picture 1
Picture_1.jpgRead Answer Items for Question 5
Picture 2
Picture_2.jpgRead Answer Items for Question 5
Capsid is composed of > 60 subunits and each subunit has an identical interaction with adjacent subunits
Read Answer Items for Question 5
Capsid is composed of 180 identical subunits in which interactions with adjacent subunits are similar, but not identical.
Read Answer Items for Question 5
Answer
A. Helical
B. Icosahedral
Question 6: Like eukaryotic genomes, viral genomes follow the “one gene, one mRNA” dogma.
Answer
- True
- False
Question 7: The diagram below depicts the typical structural elements in an enveloped DNA virus. Match each letter with the name of the structural element depicted in the diagram.
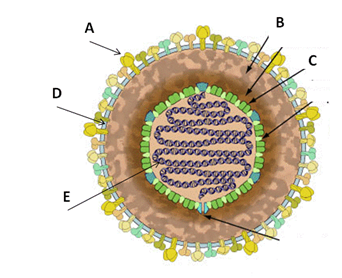
A.
Read Answer Items for Question 7
B.
Read Answer Items for Question 7
C.
Read Answer Items for Question 7
D.
Read Answer Items for Question 7
E
Read Answer Items for Question 7
Answer
I. DNA
II. RNA
III. Tegument
IV. Envelope
V. Nucleocapsid
VI. Envelope Glycoprotein
Question 8: Describe in a few sentences why it is critical for the virus life-cycle that virus structures must be stable, but not too stable. What is the technical term for this phenomena?
Question 9: Explain in 3-5 sentences why (-) RNA and dsRNA genomes must be coated with viral nucleoprotein, but (+) RNA viruses do not?
Question 10: There are known viruses for which of the following genome types (select all that apply)?
Answer
A. dsDNA
B. ss (-) RNA with DNA intermediate
C. gapped ss (+) RNA
D. ss (-)RNA
E. ss (+) DNA with RNA intermediate
F. ssDNA
G. ss (+) RNA
H. dsRNA with DNA intermediate
I. gapped (-) RNA
J. ss (+) RNA with DNA intermediate
K. gapped dsDNA
L. dsRNA
Question 11 Which of the following statements are true about virus symmetry and self assembly (select all that apply)?
Answer
A. Most viruses encode at least 10 different non-identical subunits that assemble to form the viral capsid.
B. Binding contacts between neighboring subunits are non-covalent
C. Subunit contacts are covalent
D. Each subunit has identical or similar contacts with neighboring subunits
F. Each subunit has different binding contacts with neighboring subunits.
Question 12: In addition to their discovery of the structure of DNA, Watson and Crick were the first to recognize that most viral capsids are formed by symmetrical arrangement of multiple copies of a small number of proteins. Explain in 4-5 sentences why viruses have evolved these types of symmetrical structures.
