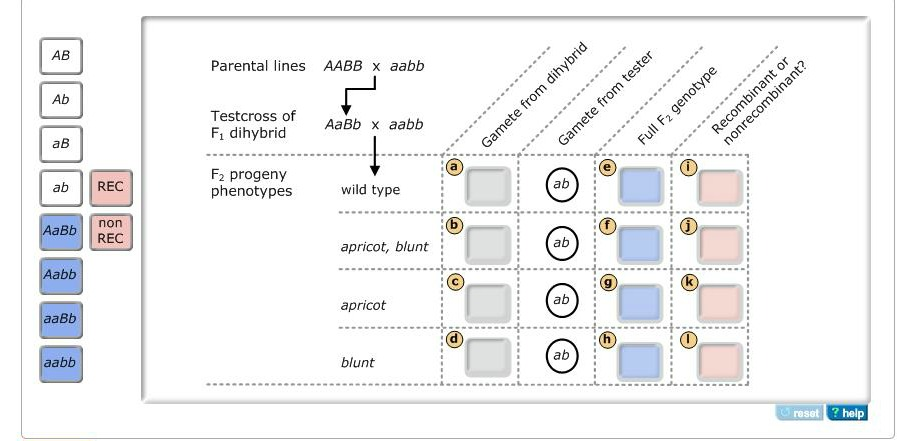
Recombination in dihybrid crosses
You have screened for several new recessive mutations in a species of wasp.
- Wasps homozygous for apricot (aa) have pale orange eyes. (Wild-type eyes are brown.)
- Wasps homozygous for blunt (bb) have short wings. (Wild-type wings are long.)
You make a pure-breeding double-mutant (apricot, blunt) line and cross it with wild-type wasps. The F1 is wild-type in appearance.
You testcross the F1 dihybrids with the double-mutant line (the “tester” genotype) and obtain four phenotypes in the F2:
- wild type
- apricot, blunt
- apricot
- blunt
Determine the following for each F2 phenotype:
- the haploid genotype of the gamete it received from the F1 dihybrid
- its full diploid genotype
- whether the gamete it received from the F1 dihybrid was recombinant (REC) or nonrecombinant (nonREC).
Complete the table by dragging the white labels to the gray targets, the blue labels to the blue targets, and the pink labels to the pink targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all.