How does the body react to rapid weight loss
Question 1: How does the body react to rapid weight loss?
Hunger decreases and the metabolic rate goes up.
Hunger increases and the metabolic rate goes up.
Hunger increases and the metabolic rate goes down.
Question 2: Which of the graphs in the figure best illustrates the activity of an enzyme as substrate concentration increases from 0 to the saturation point of the enzyme?
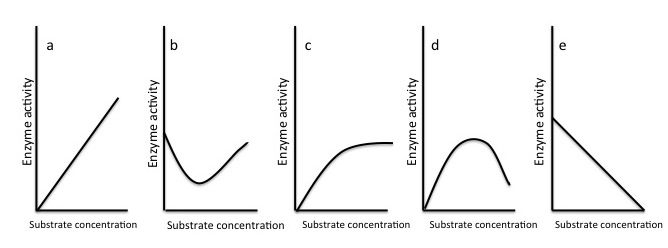
graph of substrate-enzyme activity
Question 3: What is the connection between a person’s genes and his or her metabolism?
DNA regulates metabolic pathways directly
enzymes encoded by genes regulate metabolic pathways
structural proteins encoded by genes regulate metabolic pathways
Question 4: Energy is stored in different forms in the body. ATP is very unstable and is put to use very quickly in cells. Other storage molecules last longer. Which gives the major energy stores of the body in the correct order?
Short term: fat. Medium term: glycogen. Long term: glucose.
Short term: glycogen. Medium term: glucose. Long term: fat.
Short term: glucose. Medium term: glycogen. Long term: fat.
Question 5: Which of the following are characteristics of metabolic pathways?
Contain many intermediates.
Are regulated.
Each pathway has a key enzyme that catalyzes most of the reactions
Are specific for each organism
Are often reversible
Question 6: What would be a typical regulatory system in a metabolic pathway?
The pathway’s product slows it down, so that the product is maintained at a constant level in the cell or organism.
The pathway’s product makes it go faster, so that more and more of the product builds up in the cell or body.
Question 7: In a metabolic pathway, a typical control mechanism is to have: ________
a lack of reactant stimulate the pathway.
the final product inhibit the enzyme responsible for its own production.
a reactant inhibit a late step.
the final product inhibit an early step.
Question 8: Which best describes body weight regulation in a normal human who is living in a modern society?
Our normal responses of appetite and metabolism tend to cause weight gain in modern societies, and they also tend to make weight loss difficult.
Our normal responses of appetite and metabolism ensure that adults remain at a given normal body weight. Any change from this normal weight sets in motion responses that return the body to its normal weight.
Question 9: Which of the following regulatory mechanisms is described incorrectly?
All are correct
competitive inhibitor: binds to the active site of the enzyme
substrate availability: more substrate increases enzyme activity (until it reaches saturation)
enzyme modification: enzyme gains or loses a functional group
feedback inhibition: product inhibits its own production
Question 10: The fundamental difference between competitive and non-competitive inhibition is: _________________________
the size of the active site of the enzyme.
the manner of binding of the inhibitor to the enzyme.
the manner of binding of the substrate to the enzyme.
Question 11: Imagine a hypothetical organism (critter). A DIPLOID cell from this organism has 20 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be found in a HAPLOID GAMETE of this organism?
20
10
40
46
Question 12: Imagine a hypothetical organism (critter). A DIPLOID cell from this organism has 20 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be found in a GERM CELL of this organism?
40
10
46
20
Question 13: Gametes are:
haploid
sometimes haploid and sometimes diploid
diploid
Question 14: During what stage of the cell cycle does the cell grow and carry out it regular functions?
G1
G2
Mitosis
S
Question 15: If a germ cell has 20 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will you find in the daughter cells, after meiosis?
20
40
10
30
Question 16: A muscle cell is an example of what type of cell?
a zygote cell
a somatic cell
a gamete cell
a germ cell
Question 17: If a germ cell has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will you find in the daughter cells, after meiosis?
92
46
69
23
Question 18: During the S phase of the cell cycle, DNA is replicated. What form would you expect the DNA to be in?
It would be in a loose pile.
It would be tightly wound around histone proteins as chromosomes.
It would be made of separate nucleotides just floating in the nucleus.
Question 19: During which stage of the cell cycle is the DNA replicated?
S
Cytokinesis
Mitosis
G2
Question 20: If a cell is not dividing, and has not yet begun replicating its DNA what phase of the cell cycle would it be in?
S
M
G2
G1
Question 21: An organism grows through what process?
Cellular respiration
Protein synthesis
Mitosis
Meiosis
Question 22: Cancer can be the result of all of the following EXCEPT?
A non-functional tumor suppressor gene and a non-functional proto-oncogene.
Exposure to a carcinogen.
A disregulation of the cell cycle.
A functional tumor suppressor gene and a functional proto-oncogene.
Question 23: What stage of division is this cell in?
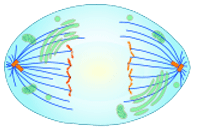
Anaphase
Prophase
Telophase
Metaphase
Question 24: What stage of division is this cell in?
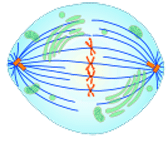
Metaphase
Telophase
Prophase
Anaphase
Question 25: The centrosome disappears and the nuclear envelopes form in what stage of mitosis?
metaphase
telophase
interphase
anaphase
prophase
Question 26: What stage of cell division is illustrated below?
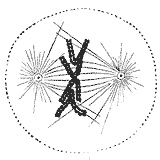
Metaphase
Prophase
Telophase
Anaphase
Question 27: Which of the following tasks is accomplished through the process of mitosis?
Replacement of dysfunctional cells
Production of sperm or eggs
Cell growth
Question 28: In what stage are sister chromatids separated and pulled to opposite sides of the cell.
telophase
interphase
anaphase
metaphase
prophase.
