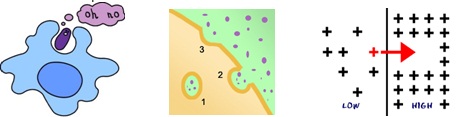
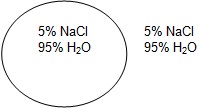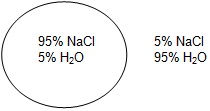Describe the processes occurring in the pictures
Part -1:
Matching: Match the phase of the cell cycle to its description and write the correct word. Some will be used more than once.
G1 S G2 G0 Prophase Prometaphase Metaphase
Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis
____________________1. Chromosomes are replicated. S
____________________2. The cytoplasm is divided. Cytokinesis
____________________3. Chromosomes “relax” into chromatin. Telophase
____________________4. The chromosomes are at the cell equator. Metaphase
____________________5. The nuclear membrane disappears from view. Prometaphase
____________________6. The spindle apparatus begins to form. Prophase
____________________7. The sister chromatids are pulled apart. Anaphase
____________________8. The kinetochores attach to the spindle apparatus
____________________9. Genes are transcribed to make mRNA.
____________________10. The cell is not dividing, although it may be metabolizing.
____________________11. The microtubules attached to kinetochores get shorter.
____________________12. A checkpoint occurs during this phase.
____________________13. Nuclear envelope forms around DNA. Telophase
____________________14. Chromatin condenses to form distinct chromosomes. Prophase
____________________15. The cell grows during this phase. G1
Part -2: Cell Transport Worksheet
Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement:
|
Statement |
Isotonic solution |
Hypotonic solution |
Hypertonic solution |
|
Causes a cell to swell |
|
|
|
|
Doesn’t change the shape of a cell |
|
|
|
|
Causes osmosis |
|
|
|
|
Causes a cell to shrink |
|
|
|
Match the term with its correct description:
a. energy e. active transport
b. facilitated diffusion f. exocytosis
c. endocytosis g. carrier protein
d. passive transport h. channel protein
________ Transport protein that provides a tunnel-like opening in the plasma membrane through which particles can diffuse
________ Is used during active transport but not passive transport
________ Process by which a cell takes in material by forming a vesicle/vacuole around it
________ Particle movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
________ Process by which a cell expels wastes from a vesicle/vacuole
________ A form of passive transport that uses transport proteins
________ Particle movement from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration
________ Transport protein that changes shape when a particle binds with
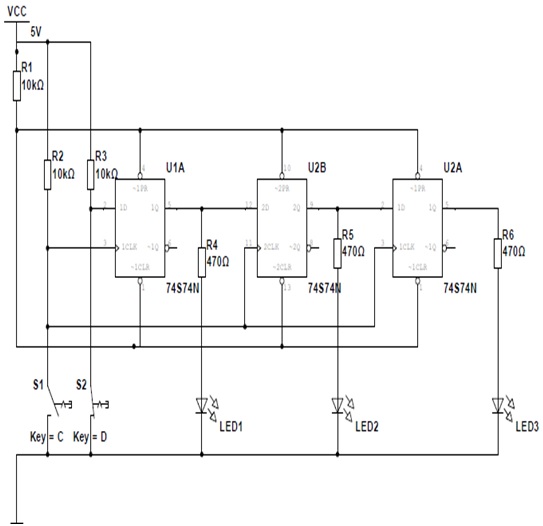
Label the diagrams of cells using the following terms: diffusion, active transport, osmosis, equilibrium. The arrows show the direction of transport. You may use the terms more than once!
Osmosis Practice Activity
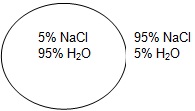
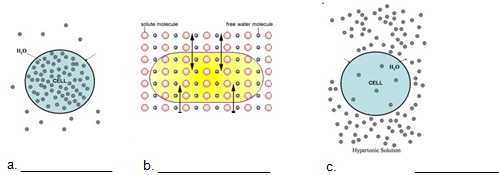
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Only water moves in osmosis! The diagrams below show the concentration of water and salt inside the cell and the concentration of water and salt surrounding the cell. Complete the sentences below by comparing the concentration of the water inside the cell and the concentration outside the cell.
| 1 |
|
a. Water will flow _____________________ (into the cell, out of the cell, in both directions). |
| b. The cell will ______________________ (shrink, burst, stay the same). | ||
| 2 |
|
a. Water will flow _____________________ (into the cell, out of the cell, in both directions). |
| b. The cell will ______________________ (shrink, burst, stay the same). | ||
| 3 |
|
a. Water will flow _____________________ (into the cell, out of the cell, in both directions). |
| b. The cell will ______________________ (shrink, burst, stay the same). |
4. At which solution of concentration gradient is each cell diagram? (Hypotonic, Hypertonic, Isotonic)
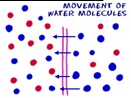
5. What does this diagram show? ___________________
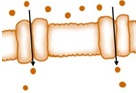
6. Using a transport protein to move particles from high to low concentration: ___________________
7. Describe the processes occurring in the following pictures: